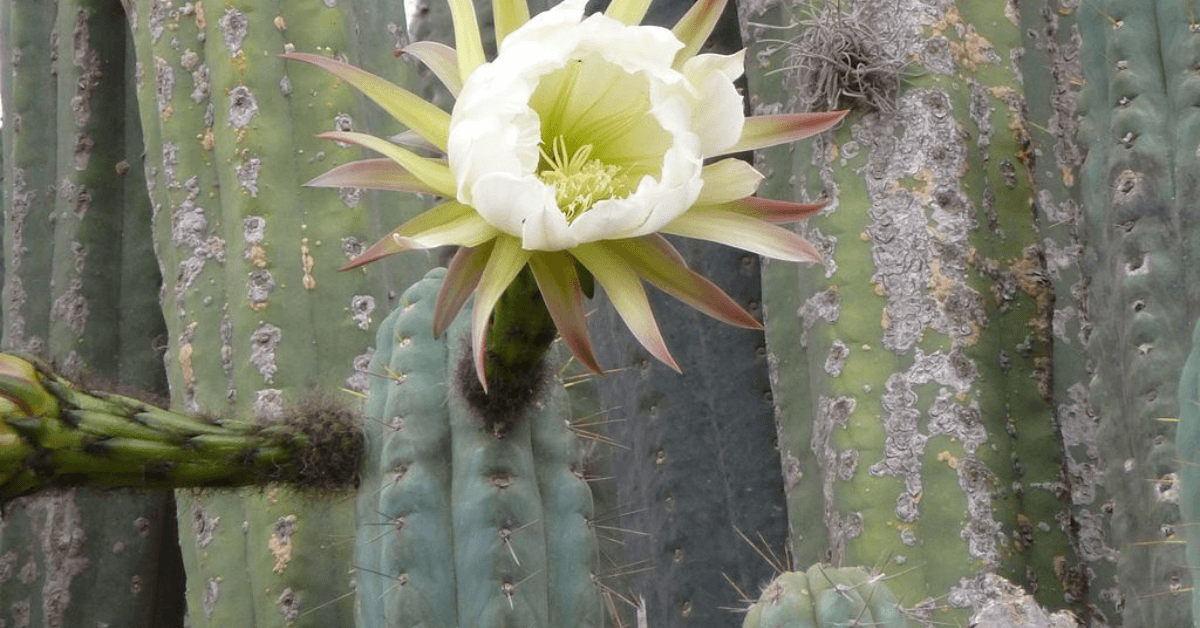
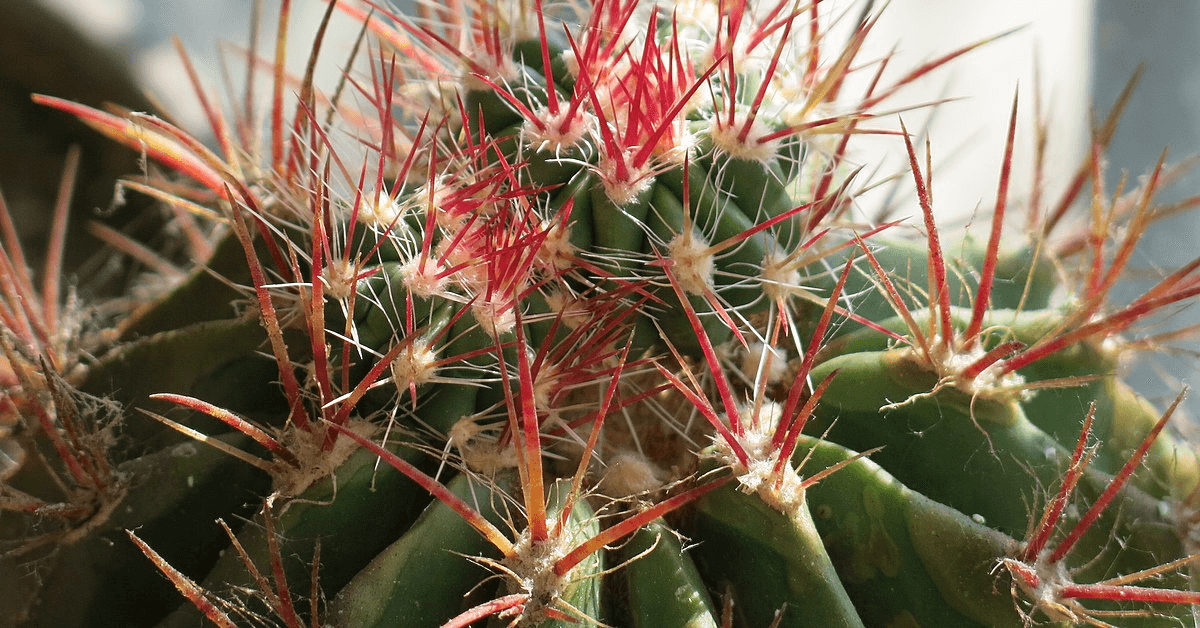
The Bolivian Torch Cactus, also known as Echinopsis lageniformis or Trichocereus bridgesii. It is a tall, columnar cactus native to the high deserts of Bolivia. It has a beautiful bluish-green color with striking white to yellow spines. This cactus can grow up to 20 feet tall in the right conditions. Other than its appearance, this cactus contains mescaline, a psychoactive compound and has been used for spiritual purposes.
Many people who want to grow and try the Bolivian torch cactus can face problems like Overwatering, Pests, Cold Temperatures, Sunburn, Nutrient Deficiency and Legal Restrictions in certain regions due to its psychoactive properties.
It’s important to check the specific laws related to growing Bolivian Torch Cactus according to your country. And follow along this article to know everything about the growing, care and uses of the Bolivian Torch Cactus.
Bolivian Torch Cactus Info
| Botanical Name | Echinopsis lageniformis (syn. Trichocereus bridgesii) | Family | Cactaceae |
| Plant Type | Cactus |
| Mature Size | 6-12 feet tall, 4-6 inches in diameter |
| Ribs | 4-8 |
| Spines | Honey-brown, 6–10cm in length |
| Sun Exposure | Full sun |
| Soil Type | Well-drained, sandy or cactus mix soil |
| Soil pH | Slightly acidic to neutral (6.0-7.0) |
| Bloom Time | Summer |
| Flowesr | large white flowers, opening at night and closing by the morning |
| Average mescaline content | 0.56% by dry weight |
| Hardiness Zones | 9-11 (USDA) |
| Native Area | Bolivian High Desert |
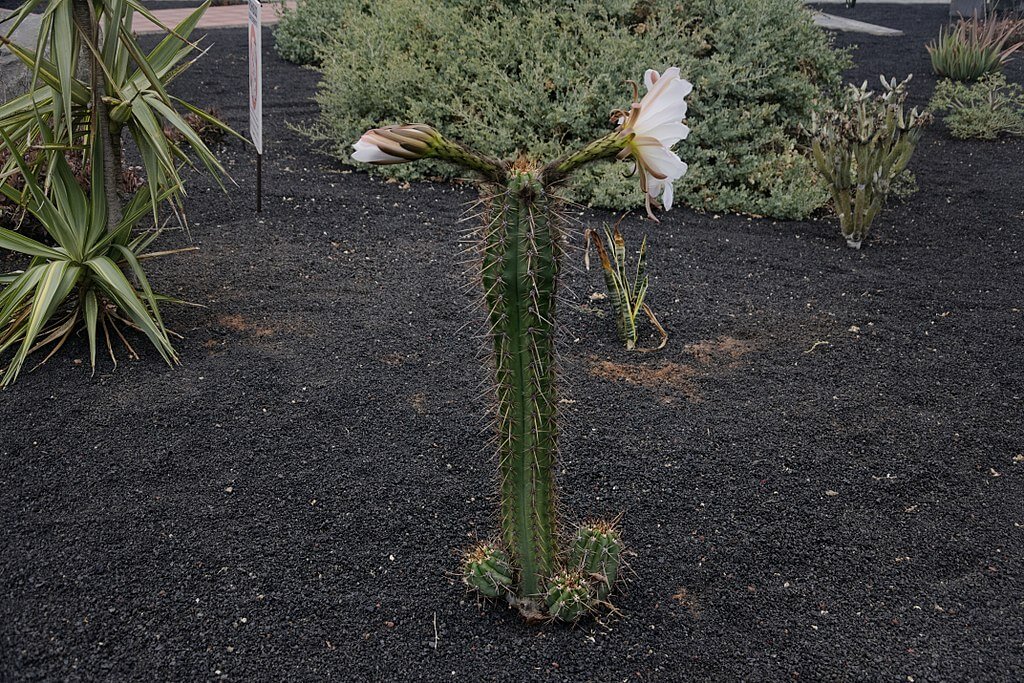

How To Grow Bolivian Torch
You can grow Bolivian torch cactus in many places providing the care it needs, but it’s important to consider its legal status, especially because it contains mescaline, a psychoactive compound.
The legal status varies by country, with some places allowing cultivation for ornamental purposes while restricting the extraction of mescaline. For example, in the United States, it is legal to grow for personal use but regulated in terms of psychoactive use.
| Method | Recommended | Difficulty | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stem Cutting | ✔ | Easy | The most common method. |
| Leaf Cutting | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | Not applicable as cacti do not propagate through leaf cuttings. |
| Seed | ✔ | Moderate | Suitable for growing many plants at once. |
| Bulb | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | Cacti do not propagate through bulbs. |
| Division | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | Not applicable for this cactus type as it does not naturally form clumps that can be divided. |
| Layering | ✘ | Hard | Not commonly used for cacti. Generally more complex and less effective compared to cuttings. |
Starting With A Cutting
- Prepare Tools and Cutting: Use a sharp, sterile knife to cut a healthy segment from an existing Bolivian Torch Cactus.
- Dry and Callous: Allow the cutting to dry and callous over for about a week. This step helps prevent rot when the cutting is planted.
- Plant the Cutting: Fill a pot with well-draining cactus mix. Plant the calloused cutting into the soil.
- Place and Care: Position the pot in a warm, bright location with indirect sunlight. Water sparingly, only when the soil is completely dry, until roots develop (typically within a few weeks).
- Monitor Growth: Once roots are established, gradually increase watering frequency.
Growing From Seed
- Prepare Seed Tray: Fill a shallow tray with well-draining cactus mix.
- Sow Seeds: Sprinkle the Bolivian Torch Cactus seeds on the surface of the soil. Lightly cover the seeds with a thin layer of soil.
- Moisturize and Cover: Mist the soil lightly with water. Cover the tray with plastic wrap to maintain humidity.
- Place and Care: Place the tray in a warm, bright location, avoiding direct sunlight. Keep the soil moist but not soggy.
- Germination: Seeds should germinate within 1-2 weeks. Remove the plastic wrap once seeds sprout. Continue to provide indirect sunlight and careful watering as the seedlings grow.
- Transplanting: Once seedlings are large enough to handle about 2-3 inches tall, transplant them into individual pots with cactus mix. Use small pots around 3-4 inches in diameter. Ensure the pots have good drainage holes.
How to Care for Bolivian Torch Cactus?
Now you have grown the Bolivian Torch Cactus and here are the descriptive care guidelines for the Bolivian Torch Cactus!
| Aspect | Ideal State | Avoid | Frequency (if applicable) | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light | Direct sunlight for several hours each day | Direct, intense sunlight (causes sunburn) | Daily | Gradually acclimate to direct sunlight to prevent sunburn. |
| Air Circulation | Well-ventilated area | Stagnant, humid air | Always | Place in an area with good airflow to prevent mold and fungal issues. |
| Soil | Well-draining cactus mix | Heavy, water-retentive soil | When planting or repotting | Use a mix specifically designed for cacti and succulents. |
| Watering | Deep, infrequent watering | Overwatering, waterlogged soil | Every 2-4 weeks | – Allow soil to dry completely between waterings. – Increase frequency in spring and autumn. – Reduce frequency in winter. |
| Fertilizer | Balanced cactus fertilizer | High-nitrogen fertilizers | Every 4-6 weeks (growing season) | Use a diluted cactus fertilizer during the growing season (spring and summer). |
| Temperature | Warm temperatures (70-85°F / 21-29°C) | Frost, extreme cold | Always | Protect from frost and bring indoors during cold weather. |
| Humidity | Low to moderate humidity | High humidity | Always | Ensure good ventilation to prevent humidity buildup. |
| Pruning | Remove dead or damaged parts | Cutting healthy growth unnecessarily | As needed | Use sterile tools to avoid introducing pathogens. |
| Repotting | Every 2-3 years, or when root-bound | Overly large pots | Every 2-3 years | Choose a pot 2 inches wider than the cactus. Use fresh, well-draining soil. |
| Pest Control | Regular inspection and prompt treatment | Neglecting infestations | As needed | Inspect regularly for pests like mealybugs and spider mites. Use appropriate treatments if pests are found. |
Conclusion
The psychotic properties of Bolivian torch cactus are traditionally used by the indigenous peoples in shamantic rituals. Shamans, or spiritual healers, consume the cactus to induce altered states of consciousness, which they believe facilitates communication with spirits, healing, and divination.
In many countries, it is illegal to grow or extract mescaline from the cactus. However, in the USA, it is legal for religious practices. It is advisable to check the legal status of psychoactive cacti by country beforehand.
And if you are good at grow this plant in your region, then follow the instructions above in the article and care for it accordingly. This plant is also popular among cactus enthusiasts for its impressive height and unique appearance.
If you find this article helpful, please let us know in the comments. Also, tell us what you struggle with the most in gardening.
Frequently Asked Questions
You Might Also Like ✾

The Cultural World Of Cacti: Art, History, And Uses

How to Grow and Care for Red Barrel Cactus

How to Grow & Care for Fire Barrel Cactus

The Kalanchoe Succulent with Yellow Flowers

The Kalanchoe Succulent with Stunning Pink Flowers

How to Propagate Zebra Succulent from Leaves